最近的

Senior high school student interested in math, hope to make math friends. lzakaria54@gmail.com

Reseña del Autor del premio Nobel

On the basis of the conclusions selectively gleaned from the history of ontological thought, it was assumed that the real geometry of the space of the Universe is the geometry of topologically fixed 3-dimensional hyper sphere. It claims that the understanding of metaphysical principles of space formation is important, resulting in the simplest mathematical approach to the calculation of actual astronomical distances. The comparisons of calculated lengths of trajectories of photons with the actual intergalactic distances reported by observers for different \(z\)-values are carried out using the selected assumptions. Photon mileage \(L_f = f (L_z, R_D)\) don't equal to the astronomical distance \(L_z\) detected by \(z\) value if \(R_D\) is the discrete quantum length of one of 4 space dimensions, associated with the curvature of space as a whole. The research concludes there is a good agreement between data obtained this way for star brightness with experimental data, when we speak about the hypothesis presupposing an accelerating growth of the Universe and abnormal brightness of supernovae; besides conclusions imply that adjustments to this hypothesis forward in the search of the values of brightness attenuation undetectable by today's tools are needed, otherwise, it could be talk about a possible expansion of our Universe in our era without accelerating.
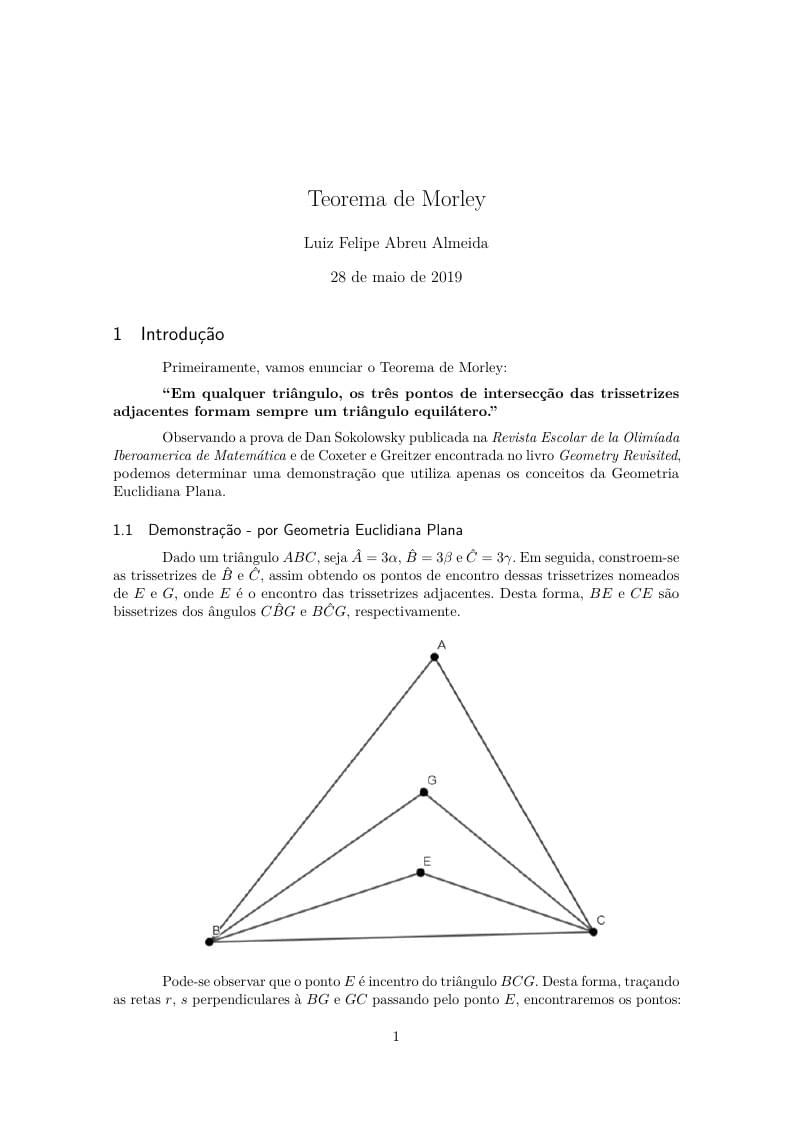
Demonstração do teorema de Morley

Prospect of IT in Bangladesh
The future of alternative energy storage for vehicles is bright because the use of hydrogen in the economy provides various solutions to environmental situations. Hydrogen is as flexible as electricity in that it can be produced in both renewable and non-renewable sources of energy. However, the literature written focuses on the conditions that are needed to be accounted for when it comes to switching to hydrogen as an alternative energy storage using statistical analysis. By taking an economic and environmental investigation, hydrogen has the best air pollution emissions in comparison to conventional, hybrid and electric vehicles. It is also found that hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are simpler in design which accounts for its weight that is much lighter than most vehicles. Ergo, hydrogen is the preferred fuel for fuel cell vehicles because of efficiency that can increase the potential for a sustainable climate.

Short biography of mathematician Emmy Noether

Visualization is a descriptive way to ensure the audience attention and to make people better understand the content of a given topic. Nowadays, in the world of science and technology, visualization has become a necessity. However, it is a huge challenge to visualize varying amounts of data in a static or dynamic form. In this paper we describe the role, value and importance of visualization in maths and science. In particular, we are going to explain in details the benefits and shortages of visualization in three main domains: Mathematics, Programming and Big Data. Moreover, we will show the future challenges of visualization and our perspective how to better approach and face with the recent problems through technical solutions.